Additive Manufacturing (AM, 3D printing), a digitally controlled manufacturing technology, is already revolutionising many industrial sectors. Transferring this potential to the large scale of construction, AM could become a key technology for the digitalisation of the construction industry, allowing new design possibilities and more efficient, resource-saving construction methods.
Together with institutes from Braunschweig and Hannover, various chairs at TUM are involved in the new Collaborative Research Centre TRR 277 “Additive Manufacturing in Construction”, funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgesellschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation).
Summary
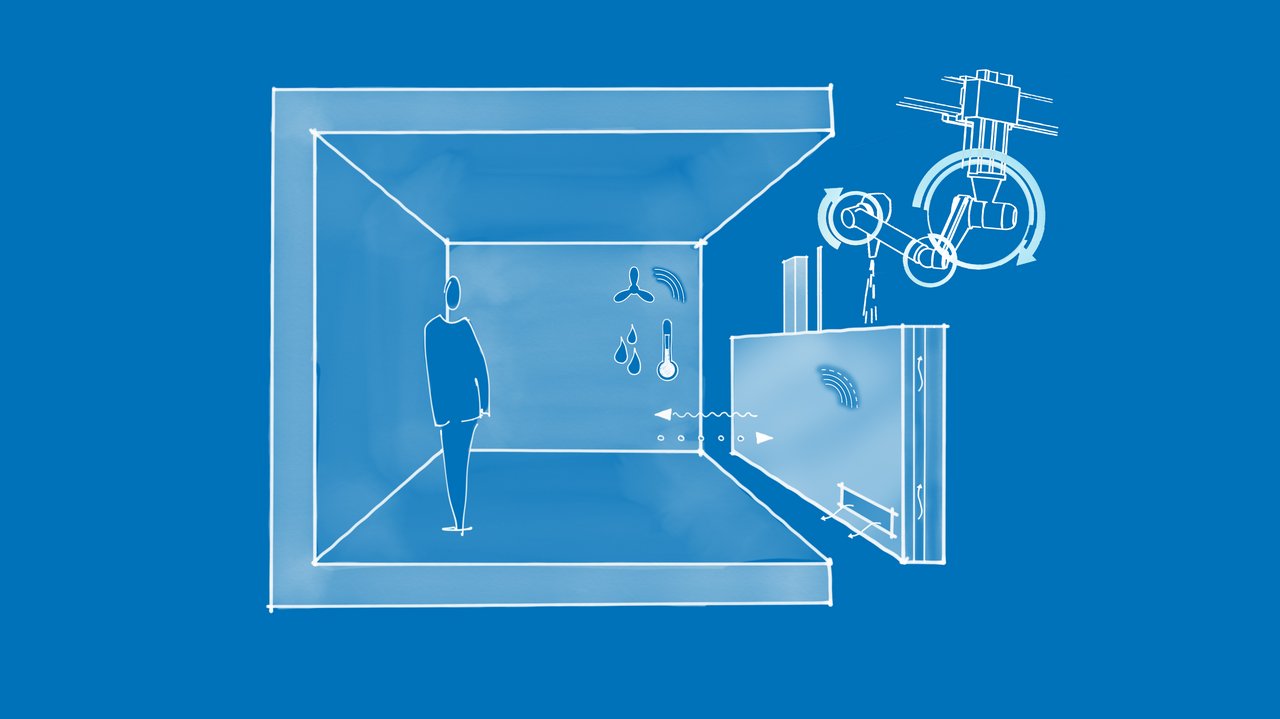
The Chair of Building Technology and Climate Responsive Design is leading a subproject within TRR 277, which aims to develop and test additively manufactured building components, that integrate multiple passive and active functions to improve building operation and environmental quality. It explores the potential of AM of building components to incorporate different performance features. The components are developed and optimised through a simulation-based parametric design process for integrated performance functionalities. This research introduces methods for a robust performance using AM building components due to the integration of passive and active functions in their design, fabrication and construction process.
Research Question
Which passive and active functions can be integrated in AM building components in different geometries and functional scenarios - considering different materials - and can their suitability be verified?
Expected outcomes:
- Analytic process to explore how complex AM component geometries can achieve both, a minimised use of material and performance optimised intrinsic characteristics.
- Methods to optimise functions, integrated in AM building components through a simulation-based process.
- Additively manufactured building components with multiple integrated passive and active functions.
Methods
- Integration and verification of multiple building technologies within the framework of a distinct construction method - Additive Manufacturing (AM).
- Methodology based on prediction of specific indoor comfort performance metrics that will be simulated considering location, function and climatic conditions according to the components’ material properties.
- Focus on the assessment of multiple requirements for passive and active building component functions.
- Simulation-based parametric design process to explore, predict and quantify the benefits from an energy and comfort related point of view for the multiple functions.
- Based on performance and potential analysis, variants are turned into physical mock-ups.
- Identify which prototypes, including its functional integrated building components, are tested under real conditions in the research and experimental laboratory.
- Manufactured prototypes are tested, using different testing protocols in order to verify and validate the various simulation models.