Living root residence
Masterarbeit von Dilara Orujzade
[Auszug]
Introduction
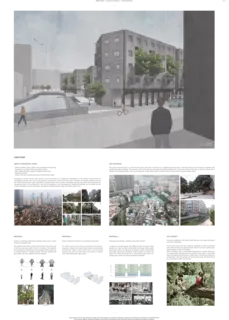
The tree used to construct Living Root Bridgesis called Ficus elastica. The goal of the thesiswas to show that Ficus elastica, and thetechniques used to build Living Root Bridges,can also be used in urban architecture. For thisthe student did a case study and designed a building inGuangzhou, a megacity in the south of China. Guangzhou has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cfa), and Ficus trees already growwell in the city. Additionally one of the projectpartners is from Guangzhou, which madethe site analysis significantly easier. In thecase study she analyzed architectual challengesspecific to her project site, and then used Ficus elastica to address these challenges.
Site Concept
Living root residence in the urbanforest: find your own space and spend your time comfortably. In the area around the site, residence buildings as well as buildings with public functions are placed densely. There is not much public space where people can feel comfortable.
With my design I give a comfortable feeling like in a forest. There you can retreat easily and spend time by yourself or with others. In the public space the feeling should be like in a light forest. It should be inviting and comfortable. In the semi-public and semi-private space, the forest should be more dense to offer more privacy.
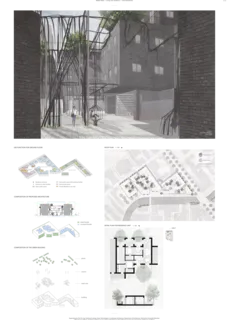
Composition of the green building
My design proposes three courtyards to provide a separation between the different types of open space. For these courtyards I use the same facade design method. For the street-facing facade, though, I use another facade design. The street facade is flat to align with the surrounding facades in harmony. In contrast, the courtyard facade faces only the private and can therefore have different volume shapes and is more flexible to build a relation between trees and people.